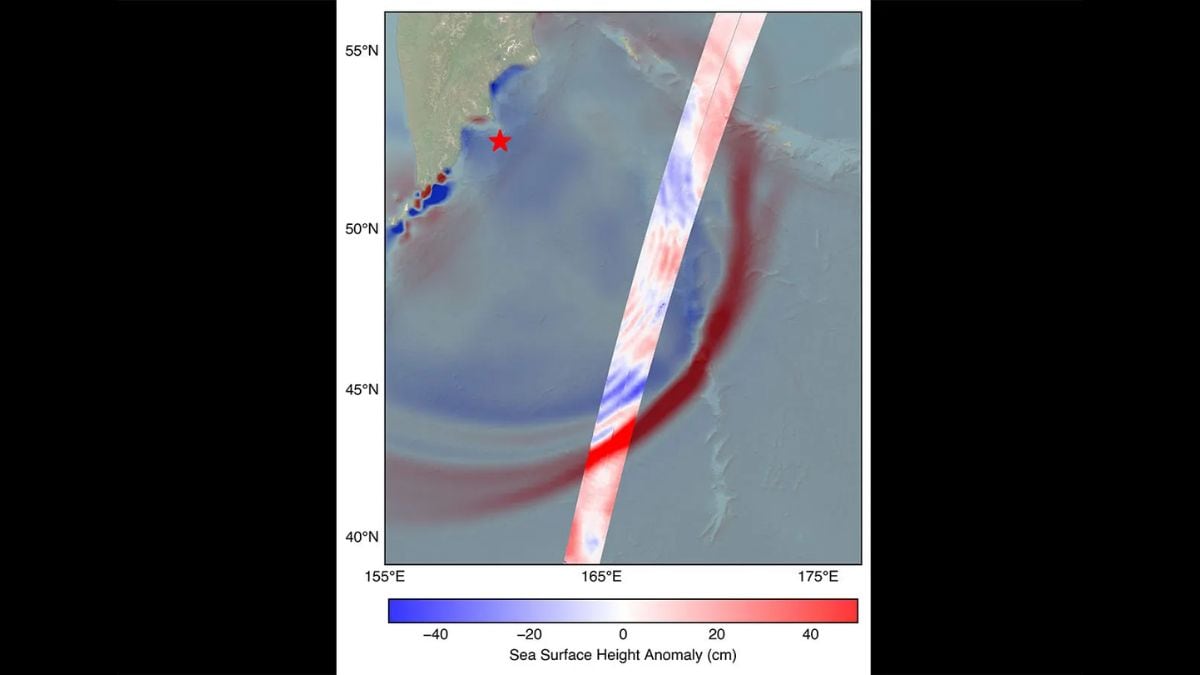

The U.S.-French SWOT (Surface Water and Ocean Topography) satellite captured the leading edge of a tsunami wave that rolled through the Pacific Ocean on July 30, 2025 (11:25 a.m. local time), in the wake of a magnitude 8.8 earthquake that struck Russia’s Kamchatka Peninsula. The satellite captured the data about 70 minutes after the earthquake struck. SWOT is a designed to map oceans and freshwater on Earth. The satellite recorded data from the tsunami as it passed through the deep ocean.
About SWOT
According to NASA, The SWOT satellite was jointly developed by NASA and the French space agency CNES (Centre National d’Études Spatiales). NASA provided the Ka-band radar interferometer (KaRIn) instrument, a GPS science receiver, a laser retroreflector, a two-beam microwave radiometer, and NASA instrument operations. The Doppler Orbitography and Radioposition Integrated by Satellite system, the dual frequency Poseidon altimeter, the KaRIn radio-frequency subsystem, the satellite platform, and ground operations were provided by CNES.
These advanced technology and specialized radar helps SWOT to map the height of the ocean surface. In this case, SWOT’s measurement of the tsunami wave’s height and shape in open water showed that the leading edge of the wave was about 1.5 feet (45 centimeters) high. It also captured the wave’s profile and direction as it traveled toward coastal areas. Such detailed measurements of a tsunami at sea are unprecedented.
Better disaster forecast
The NOAA Center for Tsunami Research tested its forecast models using the new satellite data and found that including SWOT’s measurements could significantly improve forecast accuracy. NASA oceanographer Ben Hamlington noted that even a 1.5-foot tsunami in the deep ocean can amplify into a 30-foot wave at the shore and it is important to detect it early. Vasily Titov, chief scientist at NOAA’s Center for Tsunami Research, added that these observations suggest SWOT could significantly enhance operational tsunami forecasting – a capability long sought since the 2004 Sumatra disaster.
For the latest tech news and reviews, follow Gadgets 360 on X, Facebook, WhatsApp, Threads and Google News. For the latest videos on gadgets and tech, subscribe to our YouTube channel. If you want to know everything about top influencers, follow our in-house Who’sThat360 on Instagram and YouTube.

