
OpenAI released two open-source artificial intelligence (AI) models on Tuesday. This marks the San Francisco-based AI firm’s first contribution to the open community since 2019, when GPT-2 was open sourced. The two new models, dubbed gpt-oss-120b and gpt-oss-20b, are said to offer comparable performance to the o3 and o3-mini models. Built on the mixture-of-experts (MoE) architecture, the company says these AI models have undergone rigorous safety training and evaluation. The open weights of these models are available to download via Hugging Face.
OpenAI’s Open-Source AI Models Support Native Reasoning
In a post on X (formerly Twitter), OpenAI CEO Sam Altman announced the release of these models, highlighting that “gpt-oss-120b performs about as well as o3 on challenging health issues.” Notably, both the models are currently being hosted on OpenAI’s Hugging Face listing, and interested individuals can download and locally run the available open weights.
On its website, OpenAI explains that these models are compatible with the company’s Responses application programming interface (API), and can work with agentic workflows. These models also support tool use such as web search or Python code execution. With native reasoning, the models also display transparent chain-of-thought (CoT), which can be adjusted to either focus on high-quality responses or low latency outputs.
Coming to the architecture, these models are built on MoE architecture to reduce the number of active parameters for processing efficiency. The gpt-oss-120b activates 5.1 billion parameters per token, while gpt-oss-20b activates 3.6b parameters per token. The former has a total of 117 billion parameters and the latter has 21 billion parameters. Both models support a content length of 1,28,000 tokens.
These open-source AI models were trained on mostly English language text database. The company focused on Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) fields, coding, and general knowledge. In the post-training stage, OpenAI used reinforcement learning (RL)-based fine-tuning.
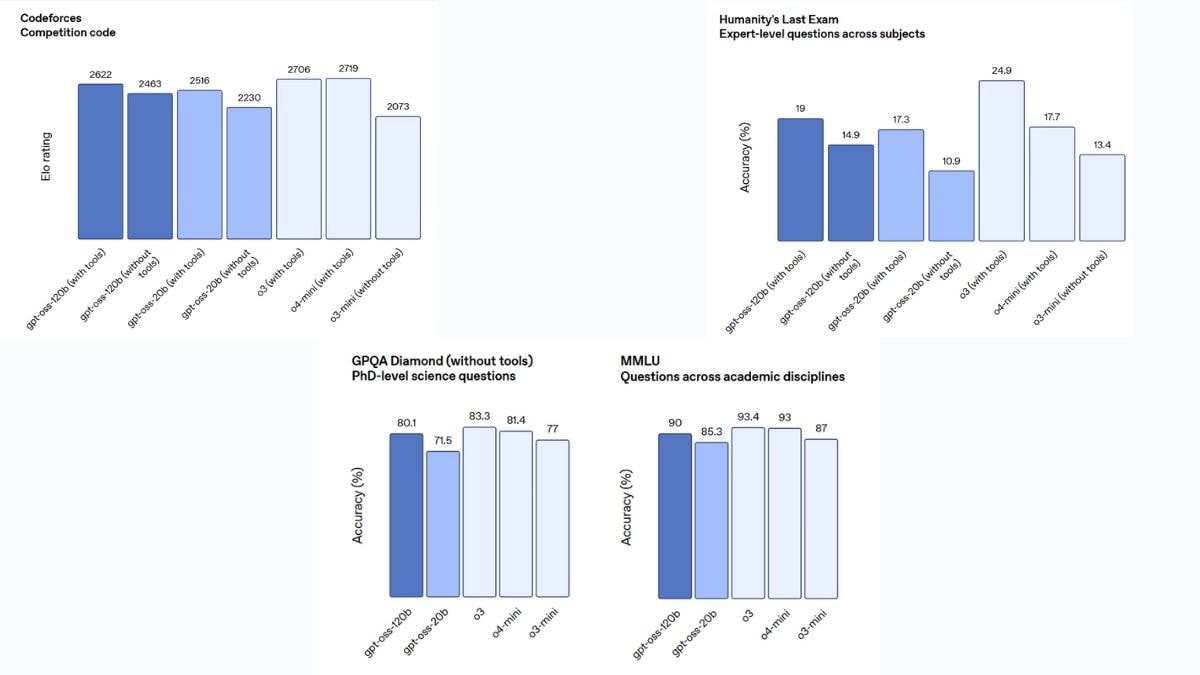
Benchmark performance of the open-source OpenAI models
Photo Credit: OpenAI
Based on the company’s internal testing, gpt-oss-120b outperforms o3-mini on competition coding (Codeforces), general problem solving (MMLU and Humanity’s Last Exam), and tool calling (TauBench). But in general, these models marginally fall short of o3 and o3-mini on other benchmarks such as GPQA Diamond.
OpenAI highlights that these models have undergone intensive safety training. In the pre-training stage, the company filtered out harmful data relating chemical, biological, radiological, and nuclear (CBRN) threats. The AI firm also said that it used specific techniques to ensure the model refuses unsafe prompts and is protected from prompt injections.
Despite being open-source, OpenAI claims that the models have been trained in a way that they cannot be fine-tuned by a bad actor to provide harmful outputs.


